-
 Rm.136,Lin he Zhong Rd. TianHe, Guangzhou, China.
Rm.136,Lin he Zhong Rd. TianHe, Guangzhou, China.
 Rm.136,Lin he Zhong Rd. TianHe, Guangzhou, China.
Rm.136,Lin he Zhong Rd. TianHe, Guangzhou, China.
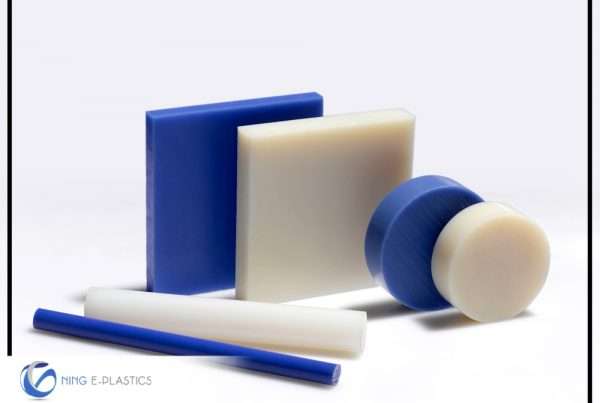


The beginning of the plastic age has made plastic a remarkable achievement and is used in all sorts of applications. Still, the scope of synthetic plastic usage was severely slow down by the less than stellar characteristics of the material. Plastic was too soft and too quick to melt until the advent of polymer technology, which gives rise to the engineering plastic.
Engineering Plastic has no precise definition, but according to analysis, engineering plastics are those who possess physical properties that enable them to perform for prolonged use in structural applications, over a wide range of temperatures, under mechanical stress, and in challenging chemical and physical environments. Some analysis shows that the long-term applicability at temperatures over 90°C up to at least 150°C is considered an important criterion. As such high-temperature resistant plastics are being regarded or called engineering plastics.
Engineering Plastic is produced in large industries with chemical certitude, enhanced with practical features; engineering plastics are manufactured to defeat corrosion as imposed by the elements, but they also resist the corrosive effects of far more caustic environments, environments that would rapidly destroy or corrode lesser materials. The same rule applies to temperature, with specialized plastic grades providing resistance in extreme environmental conditions and temperatures. Engineering Plastic may share some properties with metal, but they are fundamentally at a subatomic level. Engineered polymers created in labs are made of incredible properties that far outweigh similar properties in metal.
Engineering plastics are thermoplastics; they offer much better mechanical properties, dimensional stability, chemical resistance, durability, and much better wear and tear resistance characteristics than commodity plastics. Many engineering plastics are specifically designed to have a unique combination of properties according to the specific applications.
Engineering plastics have revolutionized the automotive industry. Components such as lightweight, impact-resistant bumpers, engine components, and interior trim benefit from the durability and versatility of these plastics. Not only do they reduce vehicle weight, improving fuel efficiency, but they also enhance safety and aesthetics.
In the aerospace sector, weight reduction is critical. Engineering plastics offer lightweight alternatives to traditional metal parts, without compromising structural integrity. Their resistance to extreme temperatures and chemicals makes them ideal for aircraft components and space exploration.
The healthcare industry relies on engineering plastics for their biocompatibility and sterilization tolerance. From surgical instruments to medical devices and implantable materials, these plastics have opened up new frontiers in patient care and treatment.
Your beloved gadgets, from smartphones to laptops, are made possible by engineering plastics. These materials provide electrical insulation, heat resistance, and structural integrity for the intricate components of modern electronics.
Engineering plastics remarkable properties continue to shape the way we live, work, and explore, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the 21st century.
Teflon and PTFE are two different names of same polymer material. To put in other words, Teflon is the trade name for PTFE. The Poly tetra fluoro ethylene (PTFE) is a unique polymer with some particular properties which are hardly or never found in any other organic polymer. That’s what distinguishes it from Teflon. Do you know what those important properties are? High chemical resistivity Lowest surface energy, & High thermal stability You might have got the gesture here, what the curtain opener is telling about! Yes, we are going to throw light on the minor differences between PTFE and Teflon today. Superficially, they both are same, but there is a slight chain of differences between both creating a thin line distinguishing both polymers in terms of their applications, features, and other specifications. Let’s take a detailed insight into both. What is PTFE? The Poly tetra fluoro ethylene is a fluorocarbon solid since it possesses high-molecular-weight compound consisting of carbons and fluorine only. It can also say to be a thermoplastic polymer consisting of just two elements: fluorine and carbon. It is a hydrophobic polymer with least amount of coefficients of friction against any solid known to anyone. This unique feature lends itself well to those applications which demand low levels of resistance. What is Teflon? Teflon is a trademark of a company spin offed from DuPont called Ken Arse. We can also call it a chain of carbon atoms that are saturated with fluorine or used two carbons being saturated with hydrogen. The Teflon is one of the most sought-after engineering plastics invented 70 years ago, and still, it is highly reputed in the market for its incredible performance in dynamic areas as compared to other engineering plastics. Difference between PTFE & Teflon in terms of Features, Uses, & Applications Features / Properties of PTFE PTFE is hydrophobic – The primary feature of PTFE is, it never reacts with water being a hydrophobic polymer material. It is also non reactant with alcohol, and other highly polar oxygen and hydroxyl-containing compounds. This property is an outcome of the high electronegativity of polymer structure. High Chemical properties – Another highlighting property of PTFE polymer is, it comprise of high chemical and corrosive resistant properties. For this reason, it has been used as pipeline coating and containers in which reactive and corrosive chemicals are required. Low tensile strength – Lastly, this polymer also comprises of high wear resistance, low tensile strength, and least creep resistance. PTFE is Non- Receptive – Since PTFE is highly non-receptive. Hence, it is used for coating surface of numerous cookwares, generally known as a non-stick skillet. Bonding Structure – The holding structure of PTFE keeps the transmission of electrons through the atomic orbital of the PTFE polymer. The holding structure of PTFE is extremely steady. Teflon isn’t exceptionally responsive to compound operators in light of the strength of the fluorine to carbon bonds. Uses of PTFE Since PTFE is a non-reactive material, perhaps due to its high strength of carbon-fluorine bonds, so it is often the choice of material utilized as a part of compartments and pipework for destructive and responsive chemicals. PTFE is also used in multiple computer applications including; coaxial cables, hookup wires, and to name a few due to its exceptional dielectric properties. Additionally, it is also utilized as a lubricant to increase wear resistance as well to reduce the friction. PTFE is utilized as a non-stick covering for skillet, cookware and even modern sustenance handling apparatus. Features / Properties of Teflon Low coefficient of friction – The Coefficient of friction actually helps in measuring how easily a standard sized material block can slide down over a flat surface of a given material. Teflon is rich in this feature – low coefficient of friction – which makes this polymer best for nonstick food cooking. Good Dielectric Properties – PTFE does not discharge electrons from the polymer orbital effortlessly because of the quality bonding between of the carbon and fluorine. This influences Teflon to have great dielectric properties and makes it a perfect protector. It is Reusable – Teflon is reusable and can keep going for quite a long time and years. These adaptable sheets can likewise be utilized to secure the base warmth platen amid sublimation or whenever there might seep around your picture. Uses of Teflon Today, Teflon is used in variety of applications including substitute bones for skull, ear parts, heart valves, tendons, nose, hip, nose, knees, dentures, sutures, and facial tracheas, as a biomedical material in fake corneas, nose cones and warmth shields for space vehicles and for their fuel tanks. The Teflon sheets can also be utilized as a weight to keep a transferring paper at its place between the warming procedures to guarantee to culminate comes about. For this reason, Teflon rod suppliers put all their efforts to make this product, a multi-functional one to make it versatile for variety of industrial, as well as medical applications. To Conclude There is not such a vast difference between both Teflon and PTFE. Though one is more dominant over other due to some highlighting features which brings it into the limelight, otherwise Teflon is just a brand name of the same polymer.
READ FULLToo much talk and discussion has been done on the significance, uses, and applications of HDPE sheets, and a person can consult best HDPE sheet supplier, it’s time to shed light upon some top most plastic and resin manufacturers who are dominating the current plastic industry. This post can be helpful for those ventures who are looking to get a deal with the top manufacturers to nail down their services in a new project. Besides, this list of top manufacturers will not only enlighten you about their core manufacturing products but also tell you about their other innovations. 1. Dow Chemical Total revenue: $49 billion It’s an American multinational synthetic organization situated in Midland, Michigan. This organization provides chemicals, plastics, and agricultural products, and it operates around 35 countries. This company is a global supplier of every major resin, polyethylene (PE), and the biggest manufacturer of polyalkylene glycols and chlorine. The principal lines of their business is based on consumer solutions, agricultural sciences, infrastructure solutions, performance materials & chemicals, and performance plastics. In 2015, the organization had yearly offers of almost $49 billion and utilized roughly 49,500 individuals worldwide. 2. Ninge Plastics Ninge plastic stands among the largest HDPE rods, tubes, sheets, and polyethylene sheet suppliers. This company believes in running a unique process than other HDPE rod and sheets manufacturers. They use premium-grade raw materials, which are strictly tested for quality and inspected to guarantee the perfectness of the product in terms of its dimensional properties. Their low friction sheets, HDPE, and PMMA rods are best for rollers and bearings due to their lightweight. HPDE is an extremely financially savvy alternative for various high-requesting modern applications. Most importantly, you can buy HDPE, Teflon, PTFE, PMMA, POM sheets, and rods from them at affordable wholesale prices worldwide. 3. Exxon Mobil Total Revenue: $236 billion It’s an American multinational gas, oil, and chemical company located at Irving, Texas, and is known to be the world’s ninth largest public company by revenue and was ranked no. 6 in sales and no. 17 in benefit all-inclusive in Forbes Global 2016 list.2 ExxonMobil produces plastics, petrochemicals, diesel, and fuel among numerous different items in every real nation of the world and investigates for oil and flammable gas in six mainland. The organization is one of the best overall makers of polyolefins and different polymers and pitches. In 2016, the organization had yearly offers of about $237 billion2 and utilized roughly 75,600 individuals around the world. 4. Lyondell Basell Total Revenue: $33 billion This company counts among the biggest plastic, and chemical manufacturing companies located in the Netherlands, and main head quarter is located in Houston, Texas, and global operations in London, UK. It basically deals in providing plastics, petrochemical products, chemicals, diesel, and gasoline among many other products which are produced in 17 countries at 55 sites. The company had annual sales of nearly $33 billion in 2015, and employed approximately 13,000 people worldwide. 5. ALPLA It’s an Austrian-based plastic manufacturing company that excels in producing blow-molded bottles, caps, injection molded parts, and tubes. This organization is the biggest maker of bundling all through Europe having 68 generation plants located in Western Europe, and holding 160 production in more than 42 countries globally. 6. Formosa Plastic Group A Taiwan plastic company that is mainly known for producing polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and some intermediate plastic goods. This company runs under the strict supervision of businessmen Wang Yung Ching, who is the founder of this company. The establishment was laid in 1954 with US $ 798,000 credit acknowledged from US help organizations. 7. LG Chemical Total Revenue: $17.8 billion This is the biggest Korean chemical company located at Seoul, South Korea. LG is a main producer of petrochemicals, polyvinyl chloride, polyolefin, manufactured rubbers and claim-to-fame polymers. Apart from it, this company also deals in manufacturing digital and IT gadgets and batteries. The company had annual sales of nearly $18 billion in 2015, and hire around 14,000 people from different corners of the world. 8. Chevron Phillips Total revenue: $13.4 billion It’s another elite petrochemical company located in Woodlands, Texas. It was established in 2000 by combining the chemical operations of both Chevron and Philips. This company deals in producing polyolefin, petrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. The organization produced about $13 billion in deals in 2014. 9. Borouge This company is the min manufacturer of polyolefin and known as a the combined venture of Borealis of Australia and Abi Dhabi international oil company. This company is involved in the business of supplying polyolefin plastics (polypropylene and polyethylene) The basic aim of expert team is to emphasize on high end applications in the Middle east, and Asia pacific with Borstar-enhanced polyethylene manufactured inn UAE, Abu Dhabi, and Borealis range of specialty products. 10. SABIC The name stands for Saudi Arabia Basic Industrial Corporation, it’s a public petrochemical company that is known to be the third-largest producer of polyethylene and fourth largest producer of polypropylene and polyolefin. Generally, this company is involved in the business of chemicals & intermediates, manufacturing polymers, fertilizers, and metals.
READ FULLHDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) sheets have become an essential material in various industries due to their exceptional strength, durability, and versatility. These sheets find applications in construction, packaging, automotive, and countless other fields. Have you ever wondered how these remarkable plastic sheets are made? We will dive into the intricate art of HDPE sheet manufacturing. From the production process to the machinery involved, we will explore the steps and techniques behind creating high-quality HDPE sheets. The HDPE Manufacturing Process Manufacturing HDPE sheets involves a series of steps and techniques that ensure the production of sheets with consistent quality and desired characteristics. Let’s explore the process in detail: Step 1: Raw Material Preparation High-quality HDPE resin pellets are selected as the primary raw material to begin the manufacturing process. These pellets are sourced from reputable suppliers and undergo meticulous quality checks to ensure their suitability for sheet production. Step 2: Extrusion Process The extrusion process is the most common technique used for manufacturing HDPE sheets. It involves the following steps: Melting: The HDPE resin pellets are fed into an extruder machine, where they are heated to a molten state. The extruder applies heat and pressure to facilitate the melting process. Mixing: During the melting stage, additives such as stabilizers, colorants, and UV protectants can be incorporated into the molten HDPE. This step allows customization of the sheet’s properties to meet specific application requirements. Shaping: The molten HDPE is then forced through a die, which imparts the desired thickness and width to the sheet. The die design can vary based on the intended application of the HDPE sheet. Cooling: As the molten HDPE exits the die, it passes through a cooling system, rapidly cooling the material and solidifying it into a sheet form. This ensures dimensional stability and prevents deformities. Step 3: Sheet Fabrication and Finishing Once the HDPE sheet is formed through the extrusion process, it undergoes additional fabrication and finishing techniques to meet specific customer needs. These may include: Cutting: The sheets can be cut into desired lengths and widths using specialized cutting equipment. Surface Treatment: Various surface treatments such as sanding, polishing, or embossing can be applied to enhance the appearance and functionality of the HDPE sheets. Edge Finishing: The edges of the HDPE sheets can be trimmed, beveled, or rounded to improve safety and aesthetics. Industrial Manufacturing of HDPE Sheets The industrial manufacturing of HDPE sheets requires advanced machinery and technology. Let’s delve into the key aspects of this process: HDPE Sheet Production Technology State-of-the-art technology plays a crucial role in producing high-quality HDPE sheets. Manufacturers utilize advanced extrusion machines with precise temperature controls, automated controls for consistent sheet thickness, and sensors to monitor key parameters. These technological advancements ensure optimal production efficiency and uniform sheet properties. Manufacturing Machinery for HDPE Sheets Specialized machinery is used throughout the manufacturing process to ensure precise control and high productivity. Key machinery used in HDPE sheet production includes: Extruder: The heart of the process, extruders are responsible for melting and shaping the HDPE resin. Dies: Custom-designed dies determine the thickness and width of the HDPE sheets. Cooling Systems: Efficient cooling systems enable rapid solidification and ensure uniform sheet properties. Cutting and Finishing Equipment: These machines facilitate the cutting, surface treatment, and edge finishing of the HDPE sheets. Molded HDPE Sheet Manufacturing Apart from the extrusion process, HDPE sheets can also be manufactured through molding techniques. Molded HDPE sheets are produced using a combination of heat and pressure, allowing for complex shapes and intricate patterns. This technique is commonly used to create three-dimensional objects or customized components with precise geometries. Techniques for Shaping HDPE Sheets The versatility of HDPE sheets lies in their ability to be shaped into various forms. Several techniques are employed to shape HDPE sheets according to specific requirements: Thermoforming: Heating the HDPE sheet and forming it over a mold to achieve the desired shape. CNC Machining: Utilizing computer-controlled machines to cut, drill, and shape the HDPE sheets with high precision. Welding and Joining: HDPE sheets can be combined using heat welding or adhesive bonding techniques to create larger structures. FAQs about HDPE Sheet Manufacturing Question #1: What are the advantages of using HDPE sheets? Answer #1: HDPE sheets offer excellent chemical resistance, impact strength, and moisture resistance. They are also lightweight, recyclable, and have good electrical insulation properties. Question #2: Can HDPE sheets be recycled? Answer #2: Yes, HDPE sheets are recyclable. They can be melted down and reprocessed to create new HDPE products, making them an environmentally friendly choice. Question #3: What are the common applications of HDPE sheets? Answer #3: HDPE sheets find applications in industries such as packaging, construction, automotive, agriculture, marine, and healthcare. They are used for products like storage containers, pipes, signage, cutting boards, and protective barriers. Manufacturing HDPE Sheets is a Complex Process HDPE sheet manufacturing is a complex process that combines advanced technology, precision machinery, and high-quality raw materials. The extrusion process and various fabrication and finishing techniques ensure the production of durable and versatile HDPE sheets. Understanding the intricacies of this manufacturing process sheds light on the remarkable properties and wide-ranging applications of HDPE sheets. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for these versatile plastic sheets will undoubtedly grow, and the art of HDPE sheet manufacturing will continue to advance, pushing the boundaries of innovation and possibility.
READ FULL